Improving Cache Placement for Efficient Cache-based Rendering
Yu-Ting Wu1 I-Chao Shen2National Taipei University2 The University of Tokyo3
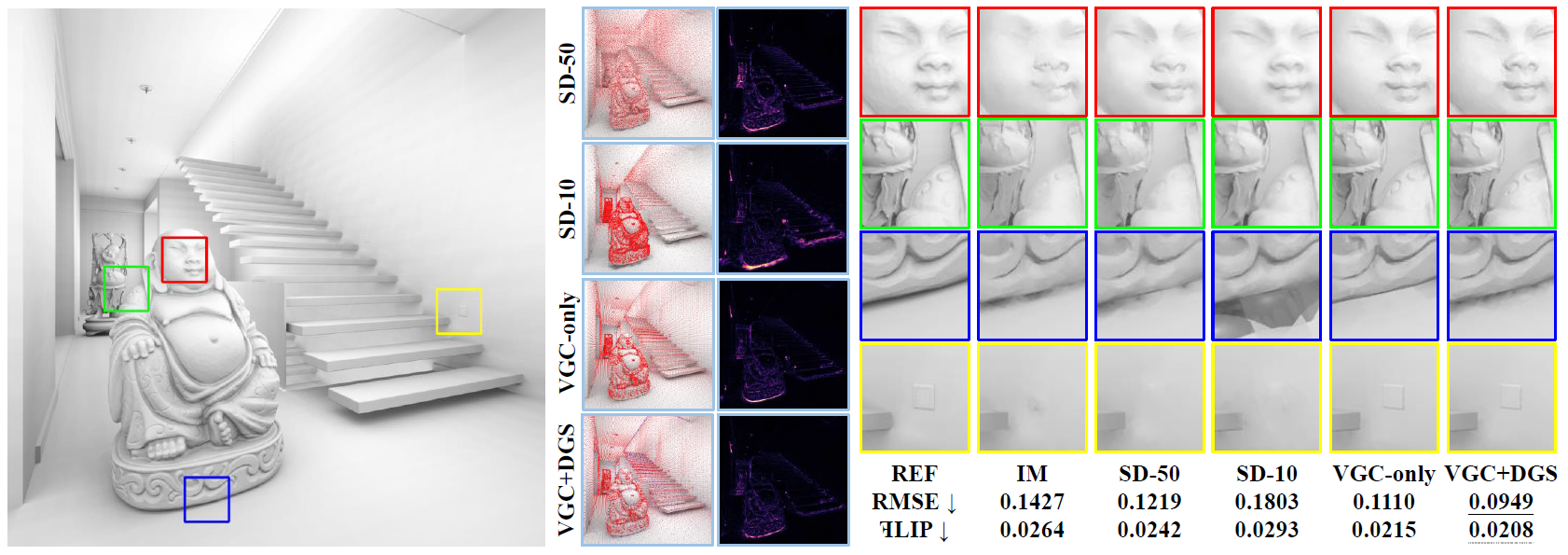
Equal-cache comparison (30K caches) on Staircase scene rendered with cached-based ambient occlusion using various cache distributions: image-space uniform sampling (IM), spatial-directional clustering [Ou and Pellacini 2011] with a minimum cluster size of 50 (SD-50) and 10 (SD-10), our view-guided clustering only (VGC-only), and our full method (VGC+DGS). The middle columns visualize each method’s corresponding cache distribution and a perceptual error computed by FLIP [Andersson et al 2021]. As shown from the right insets, image-space uniform sampling (IM) fails to capture geometric properties. Spatial-directional clustering (SD) encounters troubles in parameter selection. Using a large cluster size blurs out the details of the distant Buddha, while using a small cluster size results in large errors in near regions. Our view-guided clustering (VGC) strikes a better balance in 3D geometric proximity and image-space importance, achieving better visual quality and smaller root-mean-squared error (RMSE) and perceptual error. Our full method (VGC+DGS) with a discontinuity-guided sampling as the second pass further enhances the results, especially in regions with shading change.
Abstract
This paper proposes a new method to improve cache placement for various rendering algorithms using caching techniques. The proposed
method comprises two stages. The first stage computes an initial cache distribution based on shading points’ geometric proximity. We
present a view-guided method to cluster shading points based on their world-space positions and surface normals, while considering
the camera view to avoid producing small clusters in the final image. The proposed method is more robust and easier to control than
previous shading point clustering methods. After computing the shading functions at the initial cache locations, the second stage of
our method utilizes the results to allocate additional caches to regions with shading discontinuities. To achieve this, a discontinuity
map is created to identify these regions and used to insert new caches based on importance sampling. We integrate the proposed method
into several cache-based algorithms, including irradiance caching, importance caching, and ambient occlusion. Extensive experiments
show that our method outperforms other cache distributions, producing better results both numerically and visually.
Publication
Yu-Ting Wu, I-Chao Shen
Improving Cache Placement for Efficient Cache-based Rendering.
The Visual Computer, volume 40, pages 8173–8187, November 2024.
The Visual Computer 2024 Paper (author version, 2.5MB PDF)
Digital library