Efficient Environment Map Rendering Based on Decomposition
Yu-Ting WuNational Taipei University
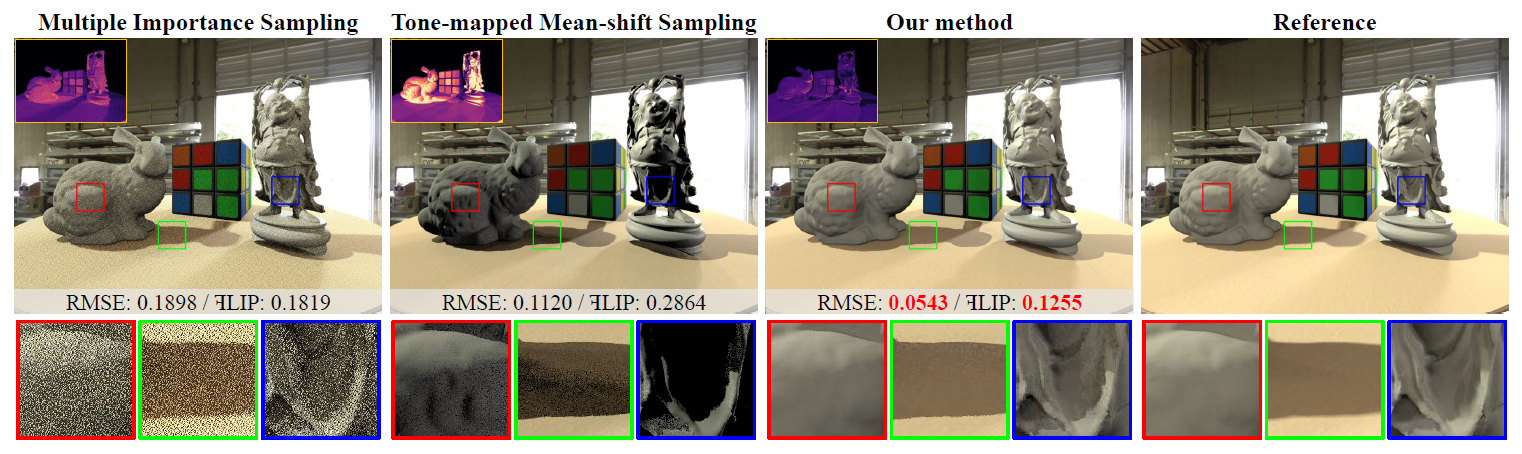
Equal-time comparisons of various environment map sampling methods. We compare our methods to multiple importance sampling (MIS) [Pharr et al. 2016] and a global sampling method based on tone-mapped mean-shift (TMMS) [Feng et al. 2016]. All methods were rendered using a CPU ray tracer [PJH16] with 4 seconds. TMMS and our method employ interleaved sampling to reduce shadow boundary artifacts caused by evaluating lighting with a small global set of lights for all shading points. Our method generates significantly less noise than MIS and renders more accurate shadows and shading than TMMS. It also achieves the lowest RMSE and FLIP [Andersson et al. 2021] errors. The error visualization of FLIP is shown in the top-left corners of the rendered images, with brighter pixels indicating larger errors.
Abstract
This paper presents an efficient environment map sampling algorithm designed to render high-quality, low-noise images with only a few light samples,
making it ideal for real-time applications. We observe that bright pixels in the environment map produce high-frequency shading effects, such as
sharp shadows and shading, while the rest influence the overall tone of the scene. Building on this insight, our approach differs from existing
techniques by categorizing the pixels in an environment map into emissive and non-emissive regions and developing specialized algorithms tailored to
the distinct properties of each region. By decomposing the environment lighting, we ensure that light sources are deposited on bright pixels,
leading to more accurate shadows and specular highlights. Additionally, this strategy allows us to exploit the smoothness in the low-frequency
component by rendering a smaller image with more lights, thereby enhancing shading accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method
significantly reduces shadow artifacts and image noise compared to previous techniques, while also achieving lower numerical errors across a range
of illumination types, particularly under limited sample conditions.
Publication
Yu-Ting Wu.
Efficient Environment Map Rendering Based on Decomposition.
Computer Graphics Forum (CGF), volume 44, issue 1, February 2025. BibTeX
CGF 2025 paper (author version, 5.4MB PDF)
Digital library
Supplemental
Additional results and comparisons (5.0MB PDF)