Learning to Cluster for Rendering with Many Lights
Yu-Chen Wang1 Yu-Ting Wu1 Tzu-Mao Li2,3 Yung-Yu Chuang1National Taiwan University1 MIT CSAIL2 University of California San Diego3
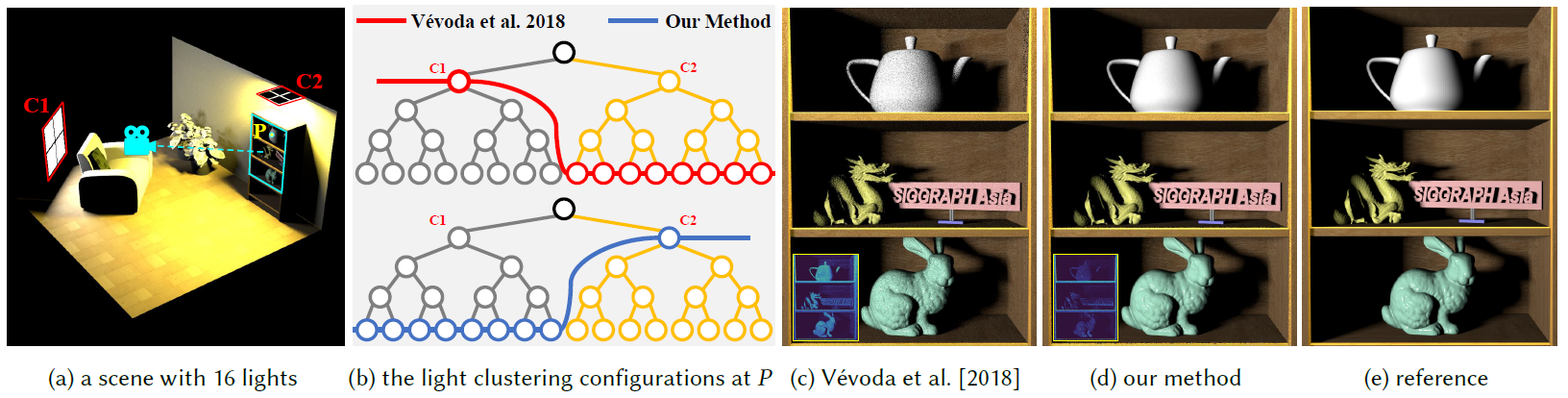
The importance of light clustering. (a) shows an example scene with 16 area lights, including 8 dull white lights on the left and 8 strong yellow lights above the bookshelf. (b) shows the visualization of the lightcuts at an interest point P. Vévoda et al.’s BORAS method [2018] constructs the cut using heuristics without considering visibility. Thus, it cannot locate the important lights within C1. By contrast, our method starts from a cut consisting of C1 and C2 and progressively refines the nodes in C1 according to the information obtained from online learning. (c) and (d) show the rendered results of Vévoda et al.’s method and our method, respectively. The error visualizations are shown at the bottom left corner. (e) shows the reference image. Our method produces an image with much fewer noises than Vévoda et al.’s method because of better adaptive light clustering.
Abstract
We present an unbiased online Monte Carlo method for rendering with many lights. Our method adapts both the hierarchical light clustering and
the sampling distribution to our collected samples. Designing such a method requires us to make clustering decisions under noisy observation, and making
sure that the sampling distribution adapts to our target. Our method is based on two key ideas: a coarse-to-fine clustering scheme that can find good
clustering configurations even with noisy samples, and a discrete stochastic successive approximation method that starts from a prior distribution and
provably converges to a target distribution. We compare to other state-of-the-art light sampling methods, and show better results both numerically
and visually.
Publication
Yu-Chen Wang, Yu-Ting Wu, Tzu-Mao Li, Yung-Yu Chuang.
Learning to Cluster for Rendering with Many Lights.
ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2021), volume 40, number 6, article 277, Tokyo, Japan, December 2021.
BibTeX
SIGGRAPH Asia 2021 Paper
Digital library
Supplemental
SIGGRAPH Asia 2021 supplementary document (0.3MB PDF)
Web interactive comparison
Last Update: September 2021